In recent years, cybersecurity has become a growing priority for business leaders, boards, and internal audit committees, with increasing investments in different areas of organizations being made for additional cyber assurance and defenses.
Despite the recent global economic downturn caused by the COVID pandemic, geopolitical conflicts, and other unforeseen situations, mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are still in full force for many industry segments. Regardless of cyclical ups and downs in the volume of transactions, M&As and divestments have become common in the modern business landscape.
In any given year, thousands of deals occur worldwide in various industries. While each case is unique, one thing remains constant: cybersecurity in M&A’s growing importance in reducing risks related to the transaction.
Traditionally, due diligence processes focused on scrutiny of long-established areas such as legal, finance, operations, business contracts, etc., with cyber risks not yet fully prioritized in acquisitions or divestments. According to Aon, as of 2020, only 10% of merger transactions involved cybersecurity in the due diligence phase. This number is expected to rise in the coming years as cyber becomes an ever-increasing topic among C-level executives and company boards.
Cybersecurity, as part of the due diligence process, helps organizations uncover any cyber risks, exposures, and liabilities; it serves as input to understand the cost of remediation and can influence the valuation or even change the course of the deal. Such assessments are crucial to provide additional insights into negotiations and reduce risks that could emerge down the line once the transaction is complete.
Failing due diligence – the Marriott case
It was one of the biggest hacks in history. In 2018, two years after hotel giant Marriott acquired Starwood Hotels, 339 million guest records were stolen from the latter’s database. Even though the hack had occurred in the Starwood database before the transaction, Marriott became liable for the breach.
In its fallout, Marriott received multiple class-action lawsuits from guests whose data had been compromised (most citing failure to perform due diligence on the sell-side’s cybersecurity), it was fined $23.8 million by United Kingdom’s Information Commissioner’s Office, and its CEO was forced to testify in front of a US Senate committee, as the hack was later revealed to be a likely Chinese government’s information-gathering operation.
While several factors had led to this data leak, what could have prevented it was a more thorough cybersecurity assessment. The due diligence process can be implemented at various stages of an M&A deal. According to a 2019 study by Forescout, 38% of respondents (senior manager-level IT and Business decision-makers) declared that they started a cybersecurity assessment already at the strategy creation step, the earliest pre-deal phase of the M&A process. 33% did so during the target screening, 22% during diligence and evaluation stage and only 6% reported performing security assessment during the integration phase.
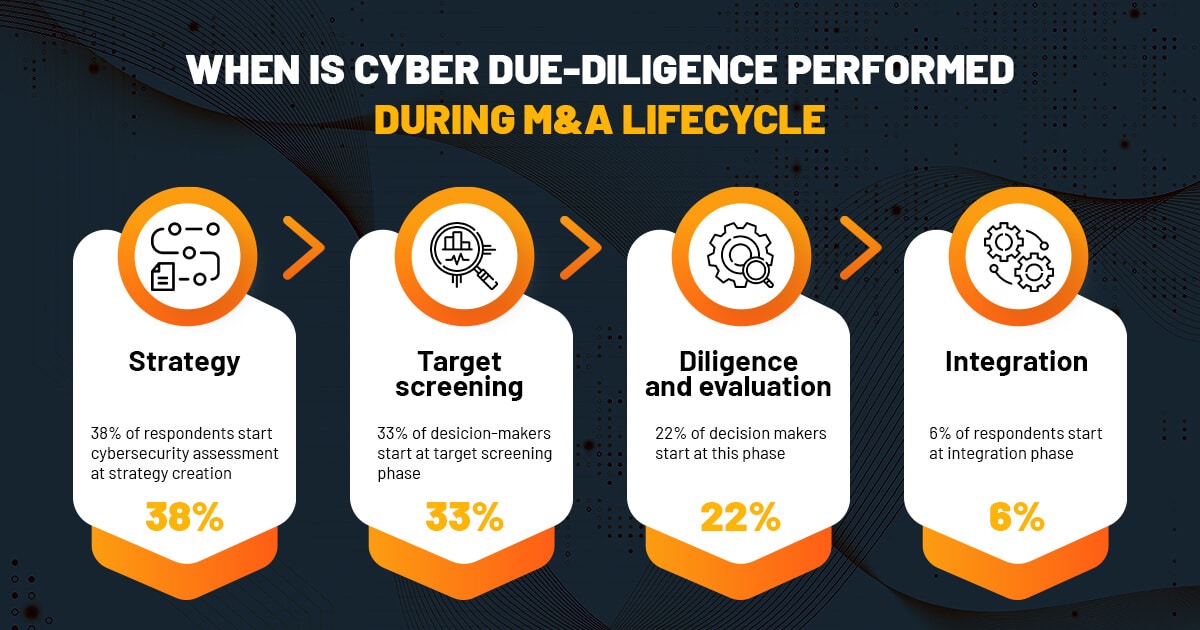
These results show that decision-makers have begun seeing the benefits of early cybersecurity review. The same study indicates that an undisclosed security issue of a sell-side can be a deal-breaker for 73% of business leaders in M&A deals.
How is technical cybersecurity due diligence for M&A performed?
Many buy-side companies hire an external contractor to execute a technical cybersecurity assessment of their target. This guarantees that the sell-side’s security controls are challenged, and its cybersecurity risks and data privacy threats can truly be revealed. The security assessment also allows the buyers to integrate the security review results into their risk analysis and even the valuation of the M&A.
Some of the actions performed as part of the cybersecurity due diligence evaluation include:
- Breach assessment: to find indicators of compromise and anomalous activities that might hint at an existing breach
- Attack surface mapping & discovery: to map the potential roads for an attack against an organization and third-party suppliers
- Penetration testing: a technical cybersecurity assessment to understand the risks of the organization’s network and main systems
- Source code security review: uncover backdoors and vulnerabilities that can sometimes only be found with access to the source code. This is usually commonplace in due diligence for tech companies whose main IP is software.
Cybersecurity in M&A – deals are becoming riskier
Purchasing a company with a compromised database or hackers already lurking in the system is not something that happened only to Marriott. Avast faced a similar issue when it bought CCleaner in 2017. That same year Yahoo’s acquisition by Verizon had a $350 million lower price tag than the initial expected value for not disclosing it had been hacked pre-transaction.
The Yahoo cybersecurity incident almost made the deal fall through, according to the news at the time, as it triggered Material Adverse Change / Effect (MAC or MAE) clauses that frequently give the purchaser the ability to exit the transaction without any further obligation.
As if M&A didn’t have enough problems, hackers are now specifically targeting companies that are looking to expand. Intending to extort ransom, they threaten to make confidential information public. Some companies targeted in 2021 were still at the private negotiation stage when the attacker managed to scan their network (using Trojan malware) for keywords such as 10-q1, 10-sb2, n-csr3, nasdaq, marketwired, and newswire, discovering they intended to make an M&A transaction.
Can such disruptions be prevented?
Lessons learned from cyber disasters in M&A
- Cybersecurity due diligence needs to be performed early – the integration stage is way too late
- Target company’s cybersecurity practices, certifications, and processes, especially those related to handling personal data, need to be thoroughly assessed
- Sell-side’s cybersecurity culture – employees’ and the board’s understanding of data security protocols is a good indicator of the company’s security risks
How Blaze can bring cybersecurity into your next M&A transaction
Working with Blaze in your next M&A project will allow your organization to negotiate more confidently. Getting a cybersecurity assessment of the target company in the due diligence stage helps your team make better-informed decisions during the merger or divestment.
We are independent experts who can provide impartial and unbiased advice for cybersecurity due diligence processes and beyond. We have proven experience working closely alongside clients in helping them better understand cyber risks in their transactions, ensuring they are all adequately documented in the data room for more accurate decisions.
Below are the solutions we offer, depending on the type of transaction and which side your organization is on.
- If you’re on the buy-side:
- Penetration testing to uncover cyber risks in the target company’s central systems
- We help your organization gain visibility into the target company’s attack surface discovery and perform vulnerability assessments, including an overview of third-party risks
- Security-oriented source code review to discover flaws and deliberate backdoors in the leading platforms and software of the target
- Continued cybersecurity evaluations during subsequent integration phases
- If you’re selling or divesting:
- Breach assessment to uncover any existing but unknown intrusions that may jeopardize the transaction or become a liability in the future
- Execution of technical measures to ensure secure data transfers, such as customer data and IP, between the businesses
- Identification of cybersecurity vulnerabilities and risks that may stem from the separation process as part of the divestiture
- Technical evaluations to ensure that the remaining company doesn’t inadvertently keep data it shouldn’t or that it wasn’t left with exposures and vulnerabilities as part of the separation
Final remarks
Mergers and Acquisitions are recovering after the 2020 slump when fewer deals were made. 2022 is expected to be a good year for the sector regardless of the economic outlook. However, with more M&A agreements being made, more cyberattacks are also likely to occur.
It is essential for business developers and M&A consultants to understand the role of cybersecurity in M&A and divestments and take the necessary steps to mitigate any risks that may compromise such transactions. A thorough independent cybersecurity assessment, either during the pre- or post-transaction stage, ensures a smooth M&A process and protects against unforeseen financial and reputational losses.








